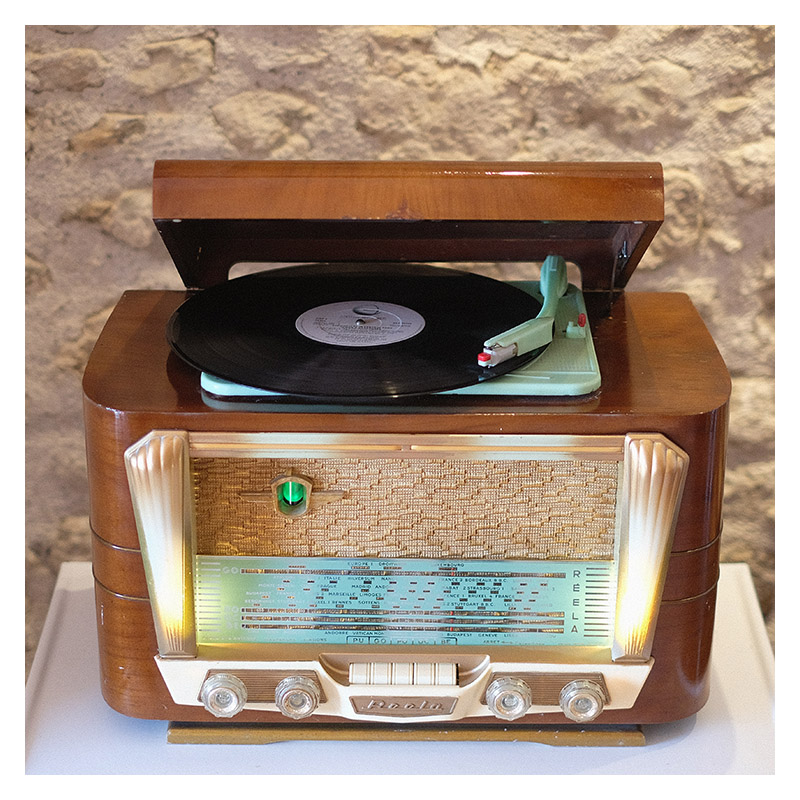
Buying a garment online is easy: you see the look, you know what material it's made of and you know your size. But buying an audio system? You can't know how it sounds. Even if we were to offer you sound samples to download, you wouldn't get any better listening than what your computer's speakers allow in terms of sound quality.
The purpose of this short article is to give you a visual idea of the sound of the devices leaving our workshop.
- Response curve of an audio system
- Two elements for comparison
- The quality of the speakers and their installation
- The digital filtering
- The High-Fidelity line
- Other factors
Response curve of an audio system
The response curve of an audio system is a graph representing the sound level achieved as a function of the frequency of the sound to be reproduced. It can be obtained by sending a signal of equal energy at all frequencies to the loudspeaker and analyzing its reproduction.
For example, for the Monacor loudspeaker studied in this article :

The yellow line modeling the cutoff has a slope of 24 decibels per octave.
As you can see, reproduction is not perfect over the 20Hz-20kHz audible range. Low frequencies are cut off (here around 100 Hz), as are high frequencies (here around 8 kHz). The central part is uneven instead of strictly flat (pronounced dip at 1 kHz and oscillations after 3 kHz).
When a loudspeaker is mounted in a cabinet to form a closed speaker, other phenomena come into play and modify the response curve. As the model of the closed cabinet detailed in this article shows, the bass is cut off at higher frequencies and the diffraction phenomenon causes new accidents:

This is a far cry from a flat response over the entire audible range (20 Hz to almost 20 kHz)!
Two elements for comparison
All the response curves published below were produced under the same conditions. They are the result of a combination of several measurements and mathematical processing designed to eliminate the effects of environmental reverberation.
Let's take as a starting point a low-end loudspeaker mounted without any particular care on a radio from the 50s:

We note that the bass cut arrives very early (around 200 Hz) and that the treble is uneven and very attenuated (-10 dB around 1500 Hz and even worse beyond 5 kHz). The sound is only well balanced between 200 and 800 Hz! However, this curve is representative of devices sold by some of our competitors...
Let's now consider the more desirable sound of a connected loudspeaker of comparable size to our radios: the Harman Kardon Onyx Studio 8. Measured under the same conditions as above, its response curve looks much better:

It's clear from this graph that listening sensations are better: bass is cut at a much lower frequency (around 50 Hz), and treble around 8 kHz, without being totally crushed at high frequencies. The midrange is also noticeably flatter.
However, the bass bump is significant (+6 dB) and may be disturbing for some listeners or musical styles, and the drop in sound level at high frequencies occurs very early.
The quality of the speakers and their installation
Since 2016, we've been constantly striving to improve the systems leaving our workshop. The first step is to select speakers that are both of good quality and suitable for the atypical cabinets we use. Then we have to find a way of integrating them neatly into the cabinet, to avoid the parasitic vibrations that will spoil the sound.
Here's what we come up with for a medium-sized radio set Ducretet-Thomson L325 :

In red: the response curve of the HK Onyx Studio 8 loudspeaker.
The bass cutoff is a little high and the high frequencies are not yet top-notch, but we have a good base to work with.
The digital filtering
Knowing the response of the loudspeaker mounted in its vintage cabinet, we can now seek to improve it. To do this, we use an electronic board on which we program a series of filters to correct the system's response. In the example above, we'll need for instance to create a combination of filters to raise the sound level between 2 and 7 kHz. The signal sent to the amplifier will thus be increased in this frequency range to compensate for the weakness of the loudspeaker.
We finally get for the Ducretet-Thomson L325 :

This corrects the midrange dip and extends the bass and treble response. If you're thinking of turning to the competitors, ask them for the response curve of their products!
The High-Fidelity line
Our sets in the "High-Fidelity" range are upgraded to two-way speakers (bass-midrange + treble), or equipped with a high-end, large-diameter full-range driver. The aim is to achieve the broadest possible response, from deep bass to extreme treble. These loudspeakers are selected after digital modeling of the cabinet to predict their optimal characteristics.
We then measure the woofer and tweeter responses separately. Specific digital filters are optimized to blend the two signals harmoniously (frequency crossover).
This is followed by the digital filtering process described above, but with a larger number of filters. The result for cathedral radio Trialmo 520 HiFi :

In red: the response curve of the HK Onyx Studio 8 loudspeaker.
The corrected response curve is very flat from 60Hz to 18kHz, so the device has nothing to envy the Harman-Kardon loudspeaker!
Sometimes you want a deeper, fuller bass. The switch on the rear panel activates the Superbass mode:

Brown: Trialmo 520 HiFi response curve without Superbass mode.
In red: the response curve of the HK Onyx Studio 8 loudspeaker.yx Studio 8.
In this way, it is possible on systems with this function to obtain heavy bass (which in this case goes down to 45 Hz). But unlike the Harman-Kardon loudspeaker, it's not compulsory!
Other factors
The aim of this article is to give an idea of the sound quality of our devices, without getting too technical. There are, of course, other parameters that we take into account to optimize the sound quality of our devices. These include :
- The phase of the sound, which should not vary too much across all frequencies.
- The choice of amplifier also plays an important role, particularly with regard to distortion.
- The system's damping time at different frequencies, which must not be too long to obtain a clear rendering of the sound track.
- Or the maximum sound level the loudspeaker can deliver.